|
Home
Services
About
Us
Projects
Contact
Us
Disclaimer
|
Unsupervised clustering
using nearest neighbor likelihood
Nearest neighbor likelihood values are computed using a critical
distance threshold. These nearest neighbor likelihood values are then
used to identify level sets that are used to find data points that are
far from points that have
previously been clustered. In this context 'far' means outside the
critical distance threshold. The first cluster is assumed to contain the
most likely data point, which is used to start the algorithm, and
approximate cluster centers are assigned as the most likely data point
in each cluster. Singleton clusters and isolated clusters containing a
small number of points are frequently found. These may be removed or
assigned to the closest cluster.
| Description |
Data |
Clusters |
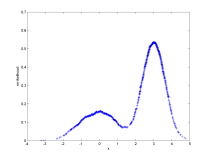
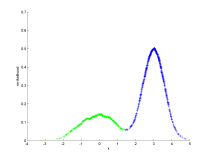
| A one-dimensional example using a mixture of two normal
distributions. The plots show the nearest neighbor likelihood
values on the y-axis for the data and the identified clusters. |
 |
 |
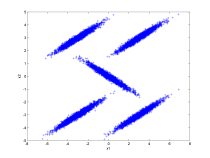
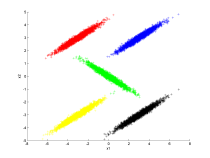
| A two-dimensional example using a mixture of five normal
distributions. |
 |
 |
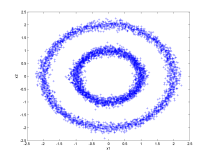
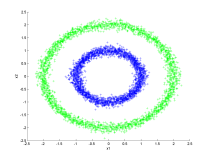
| A two dimensional example using a data set consisting of
concentric rings. These data were first converted to magnitude
values by computing their distances from the origin and then
clustered in one-dimension. |
 |
 |
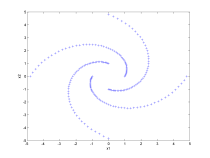
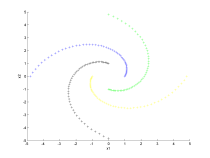
| A two-dimensional example with structured data consisting
of four spiral arms. |
 |
 |
| A three dimensional example using a mixture of five normal
distributions. |
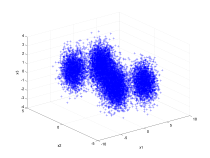 |
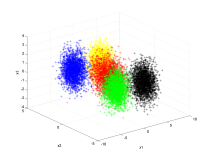 |
|