Biometrics Northwest LLC
Performing Data Analysis and Modeling
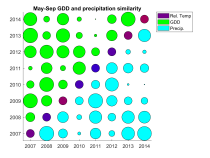
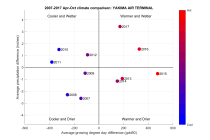
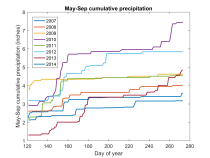
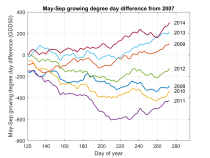
Metrics for assessing growing year climate similaritySeveral examples of metrics that may be used to compare climate variables are presented. The examples use cumulative growing degree days and cumulative precipitation during the growing season to derive metrics for the similarity of the climate variable profiles between two or more years. The growing season was defined to be from May through September, and a temperature of 50 degrees Fahrenheit was used as the base for computing growing degree days. The key metrics use the area between the climate variable profiles for two years to compute a normalized similarity value that is represented as a circle in a grid allowing two climate variable to be compared simultaneously. The diagonal of the grid is used to indicate the relative average annual temperature of each growing year that is being compared, ranging from blue to red for cold to hot years.
|
For information send email to:
info@biometricsnw.com
Last Update:
October 20, 2024
Copyright 2005-2024 Biometrics Northwest LLC